Math 112 11. Worksheet on Polynomial & Rational Inequalities
Nonlinear inequalities are all solved
using the same method because of the fact that the same rules apply for both
multiplication and division of positive and negative numbers . That is,
(+) (+) = + and (+) / (+) = +
(-)(-) = + and (-) / (-) = +
(-)(+) = - and (-) / (+) = -
So when one factor in either a polynomial
product or polynomial quotient changes sign, the entire product or quotient
changes sign.
So, all you have to do to solve nonlinear
inequalities is:
1.
Make sure there is a zero on one side of the inequality
2.
Factor the polynomial, or both numerator and denominator of the
quotient.
3.
Set each factor = 0 and solve for unknown. These solutions are called the zeros of the polynomials.
4.
Draw a number line and place every zero on the number line.
5.
Pick a number inside each interval created by these zeros and test it in
the original inequality. If a test
number satisfys the original problem then the entire interval between zeros
containing that test number is part of the solution set for the problem.
6.
After finding all such intervals , connect them with union signs ² .
Example1:
x2 > x becomes
x2 - x > 0 , which factors as
x(x-1) > 0
Now, x(x-1) = 0 has two solutions , x = 0
and x = 1. As can be seen from the
figure we have three intervals to test.
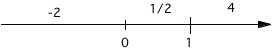
Testing x = -2 in the
original inequality we have 4 > -2 is true, so one interval of the solution
is x< 0
Testing x = 1/2 in the
original inequality we get 1/4 > 1/2 is false, so the interval from 0 to 1
is not part of the solution.
Testing x = 4 in the
original inequality we get 16 > 4,
which is true, so the interval x>1 is part of the solution. So now we can state the soluton as
x<0 ² x>1 is the total
solution to the problem.
Example 2:
(x-1)(x-2)(x+3)² 0
Example 3:
x4 - 16 ³ 0
(x - 2)2(x +
3)3(x - 4)² 0
Example 4:
![]()
Example 5:
![]()
Hwk is 1.8 1 - 10, 11 -
24, 39 - 50, but 39 - 50
are optional, just for fun.