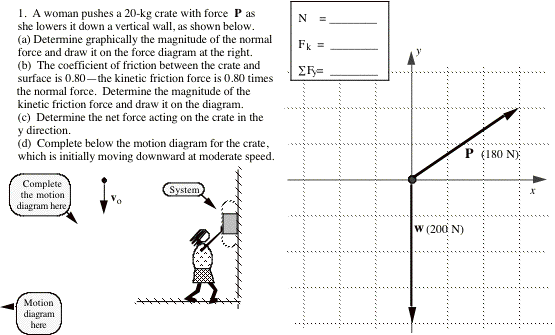
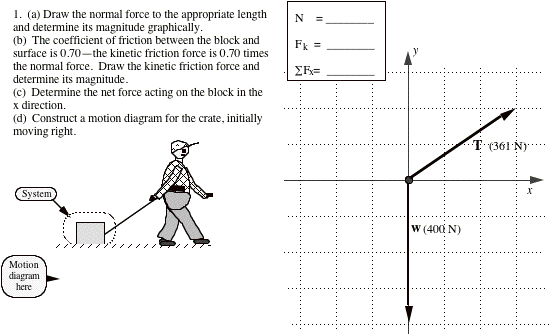
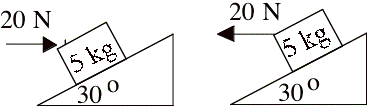
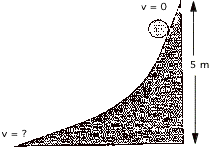
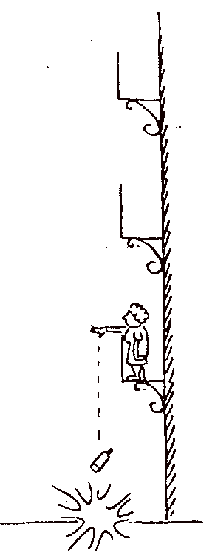
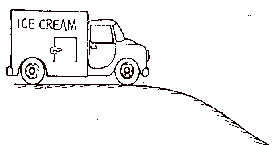
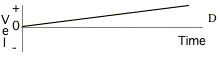Motion Diagrams
Marsha is moving upward in a hot air
balloon at 5 m/s when she drops Harry .
Draw a motion diagram for Harry beginning the instant he is
dropped. Hint: Try drawing one first beginning 10
seconds before he is dropped!


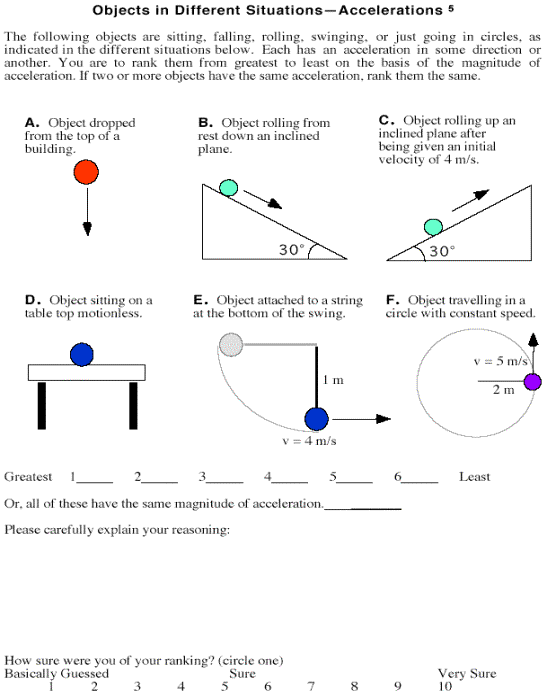
a. Draw a motion diagram of an object with
positive velocity and positive acceleration.
b. Draw a motion diagram of an object with positive velocity
and negative acceleration.
c. Draw a motion diagram of an object with
negative velocity and positive acceleration.
d. Draw a motion diagram of an object with negative velocity
and negative acceleration.
Displacement, Velocity, and
Acceleration Curves
Construct displacement, velocity and
acceleration vs time curves for :
A dog walking with constant speed away from
home.
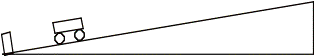
The cart given a shove then released up
the ramp below.
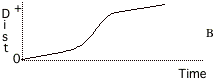
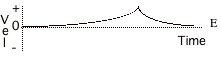
Describe the motion of the objects
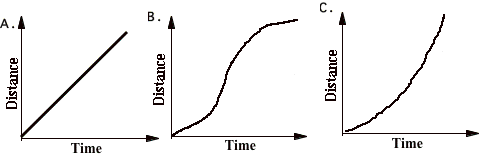
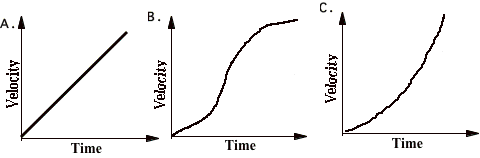
The graphs on this
page represent the motion of objects along a line which is the positive
distance (position) axis. Notice
that the motion of objects is represented by distance, velocity, or
acceleration graphs. Answer the following
questions. You may use a graph
more than once or not at all, and there may be more correct choices than
blanks. If none of the graphs is
correct, answer J. 16. Pick one graph that gives enough
information to indicate that the velocity is always negative. Pick three graphs that
represent the motion of an object whose velocity is constant (not changing). 17. 18. 19. 20. Pick one graph that definitely
indicates an object has reversed direction. 21. Pick one graph that might possibly be
that of an object standing still. Pick 3 graphs that
represent the motion of objects whose acceleration is changing. 22. 23. 24. Pick a velocity graph
and an acceleration graph that could describe the motion of the same object
during the time shown. 25. Velocity graph. 26. Acceleration graph. |
|
13. The following is a velocity-time graph
for a car.
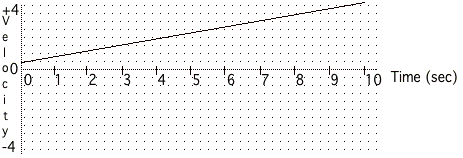
What is the average
acceleration of the car? Show your
work below.
What is the total change
in displacement of the object between time = 2 sec and time = 8 sec ?
The following is an
acceleration vs time graph for a car
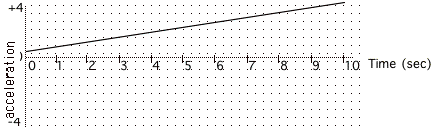
What is the total change
in velocity between t = 2sec and t = 6 sec ?
Kinematic Eq of
Motion
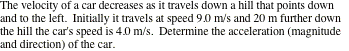
A metro train in Washington, D.C., starts
from rest and accelerates at 2.0 m/s2 for 12 s. The train travels at a constant speed for 65 s. The speed of the train then decreases
for 24 s until it comes to a stop.
What is the total distance between stops?
Projectile Motion
Chapter 4 Newton's Laws of Motion Force
and Velocity Vectors
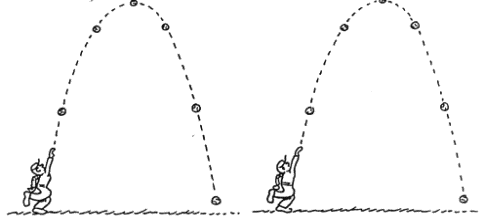
|
1. Draw
sample vectors to represent the force of gravity on the ball in the positions
shown above (after it leaves the thrower's hand). Neglect air drag. |
2.
Draw sample bold vectors to represent the velocity of the ball in the
positions shown above. With lighter vectors, show the horizontal and vertical
components of velocity for each position. Neglect air drag. |
3. (a) Which velocity component in the
previous question remains constant? Why?
(b) Which velocity component changes
along the path? Why?
Mathematical Aspects
Conceptual and physical aspects are
essential, and the best way to begin a study of projectile motion. However, projectile motion problems can
appear to be a vast array of "types" of problems to learn, unless you
get mathematical!
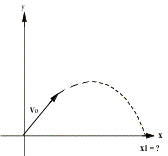
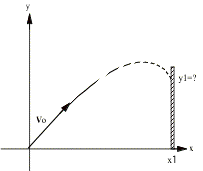
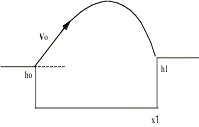
So how many different ways are there to
slice this apple, really? How many
numbers in each of the following problems?
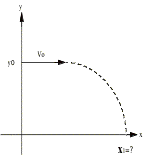

A) 5 kg Mass
B) 50 kg mass
C) They both go the same height, but it takes the 50 kg mass
longer to get to that height.
D) The both go the same height in the same time.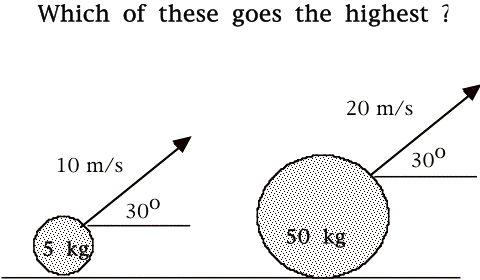
A) 5 kg Mass
B) 50 kg mass
C) They both go the same height, but it takes the 5 kg mass
longer to get to that height.
D) The both go the same height in the same time.
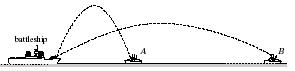
5. A battleship
simultaneously fires two shells toward two enemy ships, one
close by (A), one far away (B).The shells leave the battleship at
different
angles and travel along the parabolic
trajectories indicated below.Which
of the two enemy ships gets hit first?
Explain.