Physics 213 Final 15 Points Each December 15, 1999
Instructor: K. W. Nicholson
1. The graph below shows the position vs.
clock readings of the motion of two
trains running on parallel tracks.
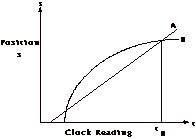
Circle all of the
following that are true:
a. at time tB
both trains have the same velocity
b. both trains speed up
all the time
c. both trains have the
same velocity at some
time before tB
d. somewhere on the
graph, both trains have
the same acceleration
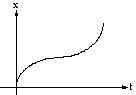
2. Describe very carefully the
motion required to create the distance vs time graph .
3. Gi-Gi, the famous Daredevil
Gazelle
has decided to try for a new gazelle distance record by being shot from a
cannon. The cannon is fired from a
platform that is 100 m off the ground.
The cannon is supposed to be aimed at an angle of 30E above the horizontal. But the guy hired to man the cannon doesn't
really know how to operate it very well, and has no common sense. He sets the dial on the declination
axis to -30Ethinking the
minus sign is just a dash, and doesn't even notice that the cannon is pointed
down 30E below the horizontal instead of instead
of up 30Eabove the horizontal. So, how far from the base of the tower
does Gi-Gi land? By the way, is
her velocity at impact greater, less than or the same as the velocity would
have been if she'd been aimed up 30E above the horizontal as intended?

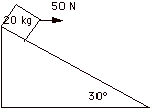
4. A 20 kg block slides down the plane. If it is pulled by a 50 N force as
indicated in the diagram below, its acceleration is 6 m/s2, what is
the kinetic coefficient of friction?
(You
must
draw a FBD to receive any credit.)
5. A 5 kg block is set into motion up an
inclined plane with an initial speed of 20 m/s. The block comes to rest after traveling 12 m up the incline,
which is inclined at an angle of 37E with the horizontal.
Find the coefficient of kinetic friction
between the block and the surface in the figure.
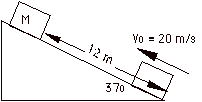
6. A 1000-kg space craft
(including missiles), coasts east at a speed of 400.0 m/s relative to the
ground. A 200 kg torpedo is fired
east at an initial speed of 600 m/s relative to the space craft. Find the final velocity of the
spacecraft.
7. A
woman whose mass is 100 kg stands
at the rim of a horizontal turntable that has a moment of inertia of 500 kg m2
and a radius of 2m. Beside her is her faithful but
very obese dog Fido, who's mass is 200 kg. The system is initially at rest, and the turntable is free
to rotate about a frictionless, vertical axle through its center. The woman
then starts walking around the rim in a clockwise direction (looking downward)
at a constant speed of 1.5 m/s relative to the earth. How fast in which direction would Fido have to walk
(at a distance of 1 m from the center)
in order to keep the turntable from rotating ?
a) What principle is involved in solving the problem?
b) Draw a picture of the situation
c) Solve the problem
8a. Identical
constant forces continuously push identical blocks A and B from the start line to the finish line. Block A is initially at rest whereas block B is initially moving right.
Which block has the
larger change in momentum?
(Circle the correct response.)
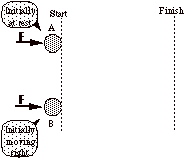
i. A
ii. B
iii. They have the same momenta change.
iv. Too little information to answer.
8b. The reason for your answer to the
question above is:
(Circle the correct response.)
(i) The same force acts on identical blocks
for the same distance
(ii) Block B already has some momentum, so
its change isn't as great.
(iii) The impulse on block B is less since
the force acts for a shorter time interval.
(iv) Block B is moving faster at the finish
line, so its change is greater.
(v) The initial and final velocities are
not given.
9.
Answer the following question about the stationary "Elevated
Lecture Beam" system shown at the right. The vertical rope is secured to a
harness about the professor's waist. The professor, (whose weight is 600 N) is
supported by the harness and by sitting on the beam at its center of mass,
(beam has a weight of 80 N). The
pulley above is frictionless.
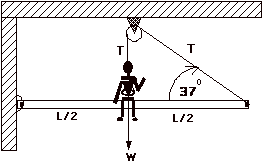
a)
Draw a FBD for the beam.
b)
Find the tension T in the
cable and the force the professor imposes on the beam.
10.
Define:
a.
Temperature
b.
Heat
c.
Internal (mechanical) energy
d.
specific heat
11. Assuming we could ignore air resistance, and that all the potential energy is turned in
to internal energy on impact, from what height would one have to drop a chunk
of ice at 0°C so that the impact with the earth would cause all of it to
turn into steam at 100°C ?
12.
In lab you heated 30 grams of 0° ice mixed with 80 grams of 0o
water until all the ice melted and
the water finally boiled.
Given that the actual value of latent heat of fusion and vaporization
for water respectively are 3.33x105J/kg and 2.26x106 J/kg, the ice
melted at time t = 120 s, the voltage and current are respectively 9V and 10 A,
the temperature was 40o C at time t = 370 s:
a) Find the experimental value Lf exp
of the latent heat of fusion for water.
b) Find the percent error in Lf exp
.
c) Find the experimental value cw exp
, of the specific heat of water.
d)
Find the percent error in cw exp .
e) Do you consider this experiment to be a
success? Explain.
13. Sketch a PV diagram and find the work done by the gas
during the following stages. (a) A gas is expanded from a volume of 1.0 L to
3.0 L at a constant pressure of 3.0 atm. (b) The gas is then cooled at constant
volume until the pressure falls to 2.0 atm. (c) The gas is then compressed at a
constant pressure of 2.0 atm from a volume of 3.0 L to 1.0 L. (Note: Be careful
of signs.) (d) The gas is heated until its pressure increases from 2.0 atm to
3.0 atm at a constant volume. (e) Find the net work done during the complete
cycle.
a)610 J, b) 0, c) -410 J, d) 0, e) 200 J
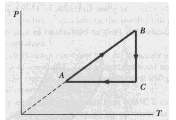
10 points Bonus!
An ideal gas undergoes the cyclic process
shown in Figure P20.36 from A to B to C and back to A. Sketch a PV diagram for this cycle.