Experiment 15a: H & T Lab 3, Heat Transfer II
What
have we done and why? We've
demonstrated experimentally that the rise in temperature of a substance is a
function of 3 things, the amount of heat input, the mass of the substance and the specific heat capacity
of the substance. In fact, we've
developed the functional relationship, namely, Q = mcDt,
where c is the specific heat capacity of the substance. In the following exercises, cups A and
B will contain water at room temperature.
The mass and final temperature of the water is as indicated in the cup in each
situation.
You
are going to first try to figure out which cup should require the most heat
input analytically, then actually perform the experiment and see if your
calculations are correct.
Pre-Lab
Situations
1 through 3 refer to two cups of water, A and B. The cups are placed in a room where the temperature is
_______oC.

______1. The
water in both cups was initially at room temperature. Cup A was heated to 75ūC and cup B was heated to 50oC. Which cup had more heat energy
transferred to it? If they both
had the same amount, say they both had the same amount of heat added.
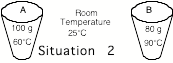
______2. The
water in both cups was initially at room temperature. Cup A was heated to 60ūC and cup B was heated to 90oC. Which cup had more heat energy
transferred to it? If they both
had the same amount, say they both had the same amount of heat added.
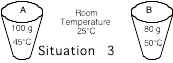
______3. The
water in both cups was initially at room temperature. Cup A was heated to 45ūC and cup B was heated to 50oC. Which cup had more heat energy
transferred to it? If they both
had the same amount, say they both had the same amount of heat added.

______4. Cup
A contains 100 grams of water and is initially at 10oC in a refrigerator. Cup A is heated until its temperature
is 30oC. Cup B contains 80 grams
of water initially at 70oC in an oven.
Cup B is heated until its temperature is 90oC. Which cup had more heat energy transferred to it? If they both had the same amount, say
they both had the same amount of heat added.
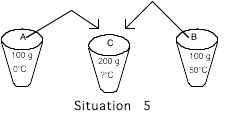
_____5. Cup
A contains 100 grams of water at 0oC and cup B contains 100 grams of water at
50oC. The contents of the two cups
are mixed together in an insulated container (no heat can transfer in or
out). The final temperature of the
water in the container is
A) Lower than 0oC E) Between 25oC and 50oC
B) 0oC F) 50oC
C) between 0oC and 25oC G) Higher than 50oC
D)
25oC
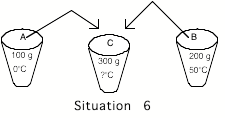
_____6. Cup
A again contains 100 grams of water at 0oC but cup B now contains 200 grams of
water at 50oC. The contents of the
two cups are mixed together in an insulated container (no heat can transfer in
or out). The final temperature of
the water in the container is
A) Lower than 0oC E) Between 25oC and 50oC
B) 0oC F) 50oC
C) between 0oC and 25oC G) Higher than 50oC
D)
25oC
Now
we'll actually obtain the amount of Qin in each of the situations 1 thru 4, and
the final temperature of the water
in situations 5 and 6, and compare these answers with our predictions.
Experiment
14: H & T Lab 3 Procedure
Start Logger Pro and Set
the time scale 0 to 500 seconds.

Situation
1: Record your experimental values, which
will be slightly different from those in the figure.
|
Cup |
mass(g) |
To |
Tf |
Dt |
V |
I |
Qin=VIDt |
Q= mcDT |
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Was
the experimental values of Q higher or lower than calculated values Q = mcDT ?
Can
you explain the difference?
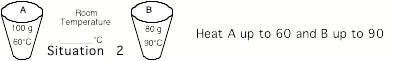
Situation
2: Record your experimental values, which
will be slightly different from those in the figure.
|
mass(g) |
To |
Tf |
Dt |
V |
I |
Qin=VIDt |
Q= mcDT |
|
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Was
the experimental values of Q higher or lower than calculated values Q = mcDT ?
Can
you explain the difference?
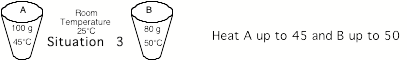
Situation
3: Record your experimental values, which
will be slightly different from those in the figure.
|
Cup |
mass(g) |
To |
Tf |
Dt |
V |
I |
Qin=VIDt |
Q= mcDT |
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Was
the experimental values of Q higher or lower than calculated values Q = mcDT ?
Can
you explain the difference?

Situation
4: Record your experimental values, which
will be slightly different from those in the figure.
|
Cup |
mass(g) |
To |
Tf |
Dt |
V |
I |
Qin=VIDt |
Q= mcDT |
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Was
the experimental values of Q higher or lower than calculated values Q = mcDT ?
Can
you explain the difference?
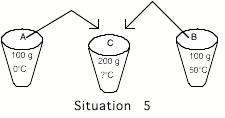
Situation
5: Cup A contains 100 grams of water at
0oC and cup B contains 100 grams of water at 50oC. The contents of the two cups are mixed together in an
insulated container (no heat can transfer in or out). Calculate the theoretical final temperature of the water in
the container. Use your
experimental values of T for A and B in this calculation.
Record
your experimental values, which will be slightly different from those in the
problem.
|
Cup |
Mass (g) |
To |
Tf |
Tpredicted |
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|
Discuss
the descrepancy (or the lack thereof) between the Tf and Tpredicted.
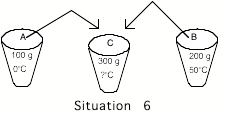
Situation
6: Cup A again contains 100 grams of water
at 0ūC but cup B now contains 200 grams of water at 50ūC. The contents of the two cups are mixed
together in an insulated container (no heat can transfer in or out). The final temperature of the water in
the container is:
Record
your experimental values, which will be slightly different those in the
problem.
|
Cup |
Mass (g) |
To |
Tf |
Tpredicted |
|
A |
|
|
|
|
|
B |
|
|
|
|