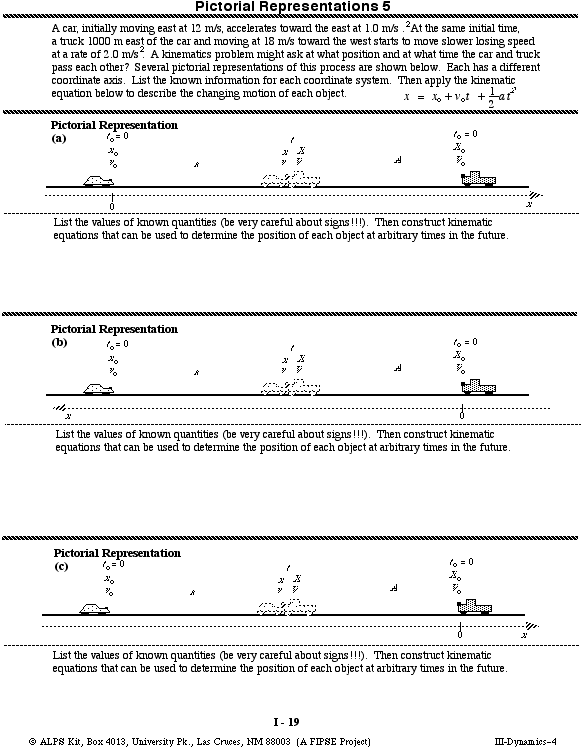
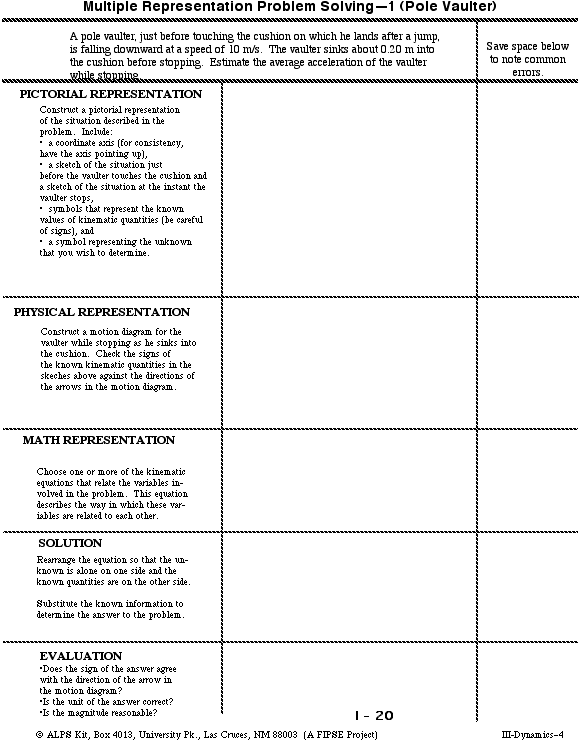
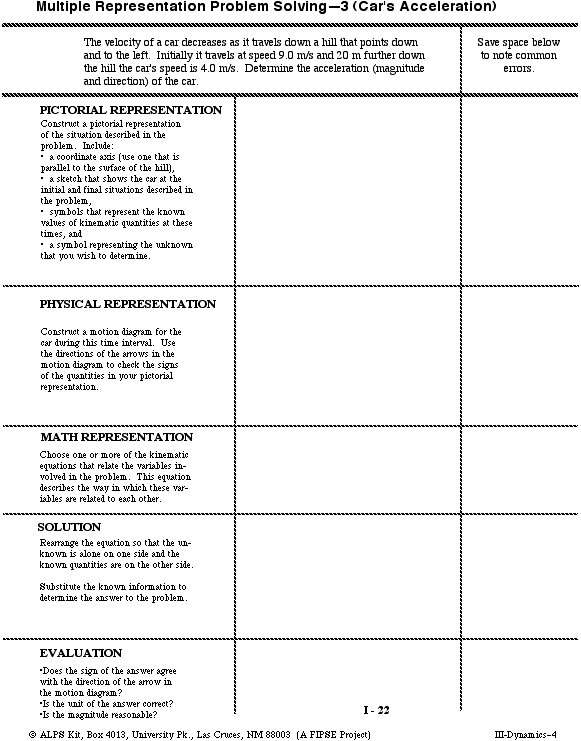
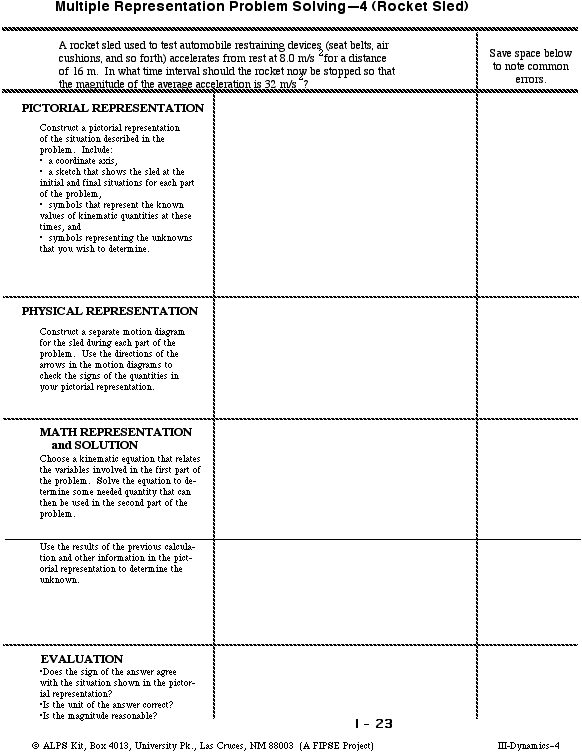
Workbook Chapter 2b Kinematics
Situations Where Acceleration is
Constant
Falling Body Problems (Plug & Chug, Oh Boy!)Discuss and Derive the
equations.
Let's do like Galileo did, slow this motion down by putting it on an
incline, so we can study it.
Demo / Groups -
• Drop a book (different sizes)
from the ceiling and obtain good data for a falling body.
• Toss up bowling ball, baseball,
and nerf ball
• Get average acceleration
• Highlite data and transfer to GA
• Look at x vs t, v vs t, a vs t,
• Discuss coefficients and what
they ought to be, then correct time and redo.
Question: So, how does the acceleration due to gravity changes for
different objects?
More questions to ponder. (Use acceleration due to gravity g= 10m/s/s)
A girl tosses a ball straight up with an initial velocity of 30 m/s.
1. How fast will it be travelling after 2 seconds?
2. How long will it take it to reach its maximum altitude?
3. How fast will it be travelling 2 seconds after it reaches its
maximum altitude?
4. How fast will it be travelling when it returns to the girl who
tossed it?
5. What is its acceleration : a) half way up, at the top, half way down
?
Workbook Activities