C&S Chapter 8 Notes
Definition: Electric Potential Voltage=
Work
done by applied force to bring test charge to that location.
Charge
= -Work
done by E-Field
Charge
Electric Potential has units of J/C,
which is called Voltage and denoted by the symbol V
RBD1 : Due
to point change Q:V(r) = ![]()
Change
in Potential = DV = -E ![]() Dr In constant
E-Field
Dr In constant
E-Field
=
-ºE¥ dr in non
constant E-Field
Comment: Recall that work is W = F¥ Dx , in like
manner, Voltage is the dot product of E and Dx
RBD2: ![]()
NOTE: to instructor : Find the work done by an applied force
to move from r1 to r2
Give values to the quantities and do
explicit problems.
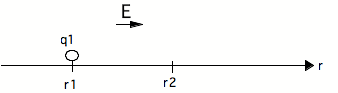
Point out how itÕs also q1DV!
RBD3: DUE = ![]() = potential energy of the system consisting of q1
and q2
= potential energy of the system consisting of q1
and q2
a
distance of r12 apart.
RBD4: If a charged particle goes in the
direction it wants to go WE > 0
DUE < 0
DV Maybe Either
RBD5: DV
when moving in the direction of E < 0.
DV when moving in the opposite direction of
E > 0.
EXERCISE:
DO 8.2.1b
DO 8.2.1c
8.2.2:
Recall
that moving sideways in g-field takes no work. The same goes for
for E-fields
8.3: DV = -ºE DL
8.4
Path independence comes from fact that dr = dl cos u
PAGE 291
Definition: Electron volt - work required to move
an electron through potential diff of 1 Volt.
qeDV = 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19J so, ![]() = 1 is the conversion ratio to convert from Joules to
electron volts (eV) and vice versa.
= 1 is the conversion ratio to convert from Joules to
electron volts (eV) and vice versa.
RBD6: DVCLD path = 0
RBD7: Vinside
metal = CONSTANT but not zero.
8.5: DO
AT HOME WIILL BE ON TEST!!!!!!!!!
(214 only)
8.5b
DVinside metal = 0 if charge is
static, if charge is moving, DVinside metal = -E ¥ dl
8.6: E
= ![]() When E constant
When E constant
DO 8.6a, b, c
E= ![]() When E not given.
When E not given.
DV = 300V
Do 8.7.1a:
FNCS = 2.4 x 10-15J
is the work done on each electron , so the potential difference between
the plates of the battery is DV = FNCS / e = ?
8.7.2: Definition
of capacitance - Charge Q on a cap
is prop to DV across capacitor. Q = CDV
Note: The units of capacitance, charge / voltage = ![]()
8.7.2a For
parallel plate capacitor 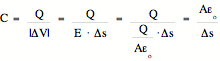
Ds = distance between plates, Q = charge on
each plate, and ![]() is the the permitivity of free space.
is the the permitivity of free space.
DO 8.7.2b If
A = 50cm X 30cm & Ds = .25mm, C=
Do 8.7.2c How
much charge Q on each plate of the 1 F caps? Q = CDV if DV = 3 V ?
(What
charge with 2 batts?)
Do 8.7.3a (214 only)
8.7.3b If r1 Å r2 ,
then r1 r2 Å
r2, etc
8.7.4a Work done on the electrons to accelerate
them is the work done by the electric field,
which is W=DK qDV = e(15000V) =
.5 mv2
v=?
8.8.1 & 8.8.2 You need to be able to
understand these in order to
Do 8.8.3a (214 only)
8.9.2 ![]()
8.9.3 ![]() q must include sign!!!!
q must include sign!!!!
8.10 C=kC0
DO 8.10.1b (214 only)
NOTE: The
easier it is to polarize a material, the greater itÕs dieletric constant.
With
this in mind, what is the dielectric constant of metal?